LEARNING OUTCOMES
‣ Provide a definition for anxiety
‣ Identify the different types of anxiety
‣ Be able to list the signs and symptoms for this disorder
‣ Describe factors influencing anxiety: biological, social, & environmental
‣ Recognize how anxiety can impact academic performance
‣ * Remember to complete the mini quiz at the end of this lesson*
———————————————————————————
DESCRIPTION
Have you ever felt nervous or had ‘butterflies’ in your stomach before a big event, like a class presentation or an important soccer game? Now, imagine that same feeling, but intensified to the point where it becomes overwhelming and disrupts your ability to function normally. Anxiety disorders can be incredibly challenging to manage because they can persistently interfere with a person’s daily life. Each person experiencing anxiety can be a result of something completely different from another person, however, overwhelming fear or uneasiness is one of the most common symptoms.
———————————————————————————
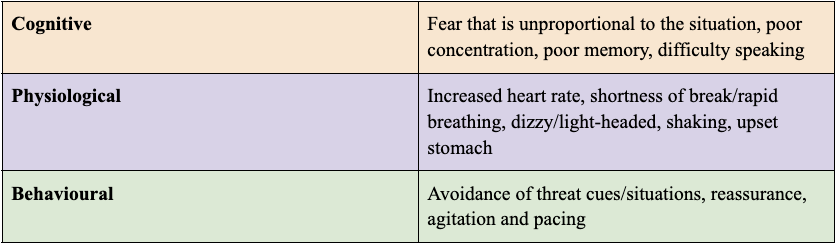
SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS
———————————————————————————
TYPES OF ANXIETY DISORDERS
Separation Anxiety: Anxiety and fear about harm to, loss of, or separation from attachment figures.
Specific Phobia: Fearful or anxious about specific objects or situations and the fear, anxiety, and avoidance are out of proportion to the actual danger posed. Different types of phobias: animal, blood-injection-injury, and situational.
Social Anxiety: Intense fear or anxiety of social situations where the individual could be negatively evaluated. This includes the fear of being embarrassed, rejected, humiliated or offending others.
Panic Disorder: Experience recurrent unexpected panic attacks and persistent concern and worry about having another panic attack. Panic attacks are abrupt surges of intense fear or discomfort that reach a peak within minutes accompanied by physical and cognitive symptoms discussed above.
Agoraphobia: Fearful and anxious in two or more of the following: using public transportation, being in open spaces, being in enclosed spaces (shops/theatres), being in a crowd.
Generalized Anxiety: The key is persistent and excessive worry about various domains including work, school performance, that are hard to control.
———————————————————————————
INFLUENCING FACTORS
Anyone can have an anxiety disorder but people who have lived through abuse, severe losses or other adverse experiences are more likely to develop one including constant stress. Further, it can run in families suggesting a combination of genes and environmental stresses.
———————————————————————————
IMPACT ON ACADEMICS
Anxiety is increasingly prevalent among postsecondary students, largely due to a combination of social and environmental factors that contribute to this mental health challenge. Many students are dealing with additional stressors such as living away from home, increased course load, navigating social opportunities, as well as working to cover tuition and living expenses. This overwhelming mix of responsibilities can make it difficult to cope, often leading to the onset or worsening of anxiety symptoms (Silva et al., 2020). Postsecondary education represents a significant departure from the comfort zone for many, marking the beginning of an independent lifestyle. Leaving behind familiar support systems and entering a new, often unfamiliar environment can make the adjustment period particularly challenging.
———————————————————————————
TREATMENT
- 1. Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors (SSRIs) are considered the first line treatment
- 2. Benzodiazepines are for short-term management and effective for panic attacks due to their fast-acting nature
- 3. Therapy that focuses on helping individuals identify and modify characteristics of maladaptive thinking patterns and beliefs that trigger and maintain symptoms
- 4. Exposure therapy can also be utilized to move individuals towards facing the anxiety-provoking situations they avoid.
- 5. Learning stress management skills such as relaxation skills and mindfulness skills can help reduce symptoms especially in real-time when you need to calm yourself down.
———————————————————————————
OTHER RESOURCES
VIDEO:
PODCAST: https://brenebrown.com/podcast/brene-on-anxiety-calm-over-under-functioning/
———————————————————————————
MINI QUIZ
Click here: Anxiety Mini Quiz
———————————————————————————
REFERENCES
American Psychiatric Association. (2022, January 13). What is anxiety? [Video]. YouTube. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=JOKS9Bx8-Sw
Brown, B. (2020, April 3). Anxiety, calm, and over-/under-functioning [Audio podcast episode]. In Unlocking us. Voxmedia. https://brenebrown.com/podcast/brene-on-anxiety-calm-over-under-functioning/
Chand, S. P., & Marwaha, R. (2023, April 24). Anxiety. National Library of Medicine. Retrieved August 13, 2024, from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK470361/
Freidman, M. (2023, September 8). Anxiety in college students: Signs, symptoms & treatments. Choosing Therapy. https://www.choosingtherapy.com/anxiety-in-collegestudents/#:~:text=The%20combination%20of%20academic%20pressure, diagnosis%20of%20an%20anxiety%20disorder
Silva, M. L., Rocha, R. S. B., Buheji, M., Jahrami, H., & Cunha, K. C. (2020). A systematic review of the prevalence of anxiety symptoms during coronavirus epidemics. Journal of Health Psychology, 26(1), 115-125. https://doi.org/10.1177/135910532095162
World Health Organization. (2023, September 27). Anxiety Disorders.https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/anxiety-disorders