LEARNING OUTCOMES
‣ Provide a definition for depression
‣ Identify the different types of depression
‣ Be able to list the signs and symptoms for this disorder
‣ Describe factors influencing depression: biological, social, & environmental
‣ Recognize how depression can impact academic performance
‣ * Remember to complete the mini quiz at the end of this lesson*
———————————————————————————
DESCRIPTION
Depression is a common and serious mental disorder that significantly impacts a person’s mood, feelings, thoughts, behaviors, and overall outlook on life. According to Statistics Canada, 7.6% of Canadians will experience some form of mood disorder at some point in their lives (Stephenson, 2023). While it’s normal to feel sad or out of sorts occasionally, a diagnosis of depression is made when symptoms persist for most of the day, nearly every day, for more than two weeks, and result in noticeable changes in day-to-day functioning.
———————————————————————————
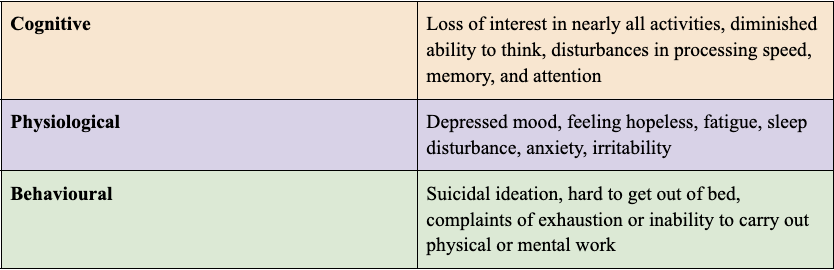
SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS
———————————————————————————
TYPES OF DEPRESSIVE DISORDERS
Seasonal Depression: People with SAD experience mood changes and symptoms similar to depression. The symptoms usually occur during the fall and winter months when there is less sunlight and usually improve with the arrival of spring. The most difficult months for people with SAD in the United States tend to be January and February. While it is much less common, some people experience SAD in the summer.
Bipolar Disorder: Bipolar disorder is a brain disorder that is associated with changes in a person’s mood, energy, and ability to function. People with bipolar disorder experience intense emotional states that typically occur during distinct periods of days to weeks, called mood episodes. These mood episodes are categorized as manic/hypomanic (abnormally happy or irritable mood) or depressive (sad mood). People with bipolar disorder generally have periods of neutral mood as well.
Persistent Depressive Disorder: A person with persistent depressive disorder has a depressed mood for most of the day, for more days than not, for at least two years. Because these symptoms have become a part of the individual’s day-to-day experience, they may not seek help, just assuming that “I’ve always been this way. ”The symptoms cause significant distress or difficulty in work, social activities, or other important areas of functioning. While the impact of persistent depressive disorder on work, relationships and daily life can vary widely, its effects can be as great as or greater than those of major depressive disorder.
———————————————————————————
INFLUENCING FACTORS
Biochemical: Chemical imbalances in the brain
Genetic: Depression can run in families
Environmental: Continuous exposure to violence, neglect, abuse, poverty
———————————————————————————
IMPACT ON ACADEMICS
Mental health challenges can significantly impact a student’s energy, concentration, mental ability, optimism, and overall outlook, all of which are essential for academic success. Research indicates that depression is linked to lower grade point averages along with higher dropout rates, and when depression and anxiety co-occur, the negative impact on academic performance can be even more pronounced. Academic pressure is a major factor contributing to student burnout. The heavy workload, coupled with the need to complete a degree as efficiently as possible to minimize costs beyond tuition, can be overwhelming. For students studying away from home, the desire to finish their degree and return home—free from the financial burdens of rent, groceries, and work—can create additional stress. This constant pressure, combined with the personal growth expected during this time, often pushes students to their limits, leading to depression.
———————————————————————————
TREATMENT
- Depression is among the most treatable of mental disorders. Between 70% and 90% percent of people with depression eventually respond well to treatment.
- 1. Antidepressants may produce some improvement within the first week or two of use yet full benefits may not be seen for two to three months. If a person feels little or no improvement after several weeks, their psychiatrist/healthcare professional may recommend adjusting the dose, adding a new medication, or switching to an alternate antidepressant
- 2. Therapy that focuses on recognizing and correcting unhealthy thinking patterns with the goal of changing thoughts and behaviors to respond to challenges in a more positive manner. It may be used alone or in combination with antidepressant medication
———————————————————————————
OTHER RESOURCES
VIDEO:
PODCAST:
———————————————————————————
MINI QUIZ
Click here: Depression Mini Quiz
———————————————————————————
REFERENCES
American Psychiatric Association. (2024, April). What is depression? https://www.psychiatry.org/patients-families/depression/what-is-depression
Kennedy, S. H. (2008). Core symptoms of major depressive disorder: Relevance to diagnosis and treatment. Dialogues in Clinical Neuroscience, 10(3), 271-277. https://doi.org/10.31887/DCNS.2008.10.3/shkennedy
Stephenson, E. (2023, September 22). Mental disorders and access to mental health care. Statistics Canada. https://www150.statcan.gc.ca/n1/pub/75-006-x/2023001/article/00011-eng.htm
Suicide Prevention Resource Center. (2020, September). Consequences of student mental health issues. https://sprc.org/settings/colleges-and-universities/consequences-of-student-mental-health-issues/#:~:text=Research%20suggests%20that%20depression%20is,anxiety%20can%20increase%20this%20association.&text=Depression%20has%20also%20been%20linked%20to%20dropping%20out%20of%20school.&text=Many%20college%20students%20report%20that%20mental%20health%20difficulties%20interfere%20with%20their%20studies.
Sutton, S. (Host). (2024, March 16). High-functioning depression & trauma in college students feat. judith joseph (No.183) [Audio podcast episode]. In She Persisted. https://player.captivate.fm/episode/966a0af8-c311-4854-ad13-8bb34c7f014f