LEARNING DESIGN
Description and Rationale: Behaviourism
Behaviourism, a learning theory that emphasizes reinforcement and feedback to shape learners’ habits, is particularly well-suited for addressing the topic of Mental Health and Well-Being. By structuring this learning resource using a behaviourist approach, we can provide clear, measurable outcomes and consistent reinforcement, which are essential for establishing healthy mental health practices. Given that this course does not require prior knowledge, we determined that cognitivism, which involves integrating new information with existing understanding, would not be as effective. Furthermore, since the course aims to dispel misconceptions and build a solid foundational knowledge about mental health and well-being, constructivism, which relies on learners’ experiential learning and practical activities, is not appropriate. The behaviourist approach ensures that learners receive the necessary reinforcement to correct false beliefs and adopt accurate, beneficial mental health practices.
———————————————————————————
LEARNING THEORY
Description and Rationale: Direct Instruction
Behaviourism in education speaks to how individuals interact with their environment and external stimuli. Specifically, learning occurs through the means of conditioning via reinforcement and feedback in order for the correct, desired response to occur in the presence of a particular stimulus (Adams, n.d.). For example, this would look like identifying an effective coping strategy (i.e. 5-4-3-2-1 method) for an anxiety attack. An instructional approach based on behavioural theory is direct instruction.
Direct instruction is designed for teaching basic skills and is useful for all learners when the material is new and difficult to grasp at first. The topic for my groups Interactive Learning Resource is Mental Health and Well-Being of Post-Secondary Students in Canada. Students come from diverse backgrounds with unique life experiences, thus this topic may be new, they may have preconceived beliefs or misconceptions, or it may be a difficult topic to explore. As a result, direct instruction would serve as an appropriate and effective instructional approach to achieve mastery in foundational knowledge for this topic in the targeted demographic.
———————————————————————————
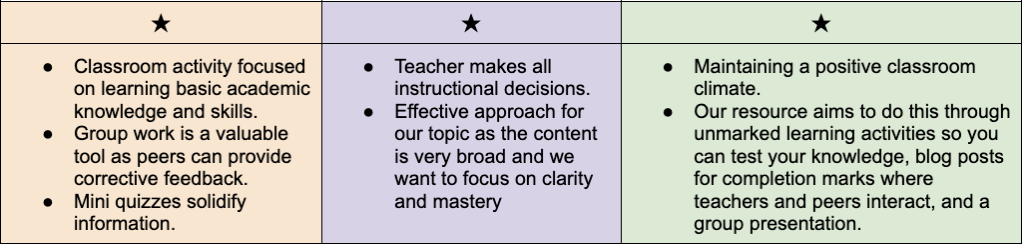
A synthesis was derived for the main characteristic of direct instruction into the following three points:
———————————————————————————
Joyce and Weil (2004, as cited in Adams, n.d.) identified five general components effective teachers employ for direct instruction. These will aid in forming an outline for how we structure our learning resource.
⭑ Orientation
◦Teacher provides an overview of lesson, importance of material, relating material to earlier lessons or life experiences, and the level of performance expected to be exhibited
◦In the learning resource this would look like including an overview of why the topic is important, listing learning outcomes, applying material to real life scenarios, and utilizing mini quizzes so learners can check their level of understanding
⭑ Presentation
◦ Breaking material down into small, easy-to-learn steps for mastery
◦ Last step is to evaluate students’ understanding
◦ This is crucial when aiming for mastery and creating a strong foundation of knowledge on a sensitive topic. In the learning resource, content would be broken down in similar ways to ensure consistency
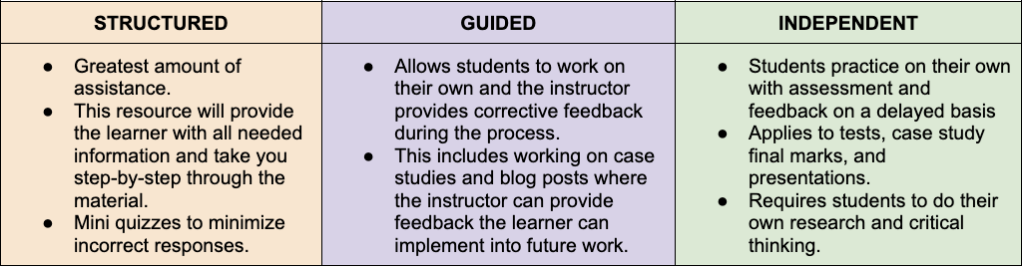
⭑ Structured, Guided, and Independent Practice
◦ Different levels of assistance